About CCS Baltic Consortium
Project applicants
CCS Baltic Consortium project (Project) is primarily aimed at significantly decreasing CO2 emissions originating from two EU Member States – Lithuania and Latvia, through CCS. The Baltic States currently do not have CO2 transport and sequestration infrastructure and are one of the last coastal territories in Europe where such system has not yet been developed or planned. Therefore, the Project wants to fill this gap by developing a robust and sustainable CO2 value chain that may be utilised by all emitters in the Baltics, thus having significant decarbonisation potential for the region.
The European Union is among the forerunners in tackling the emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) with an ambitious goal of becoming climate neutral by 2050. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is well understood and an essential instrument for reaching decarbonisation targets, primarily in hard to abate sectors emitting large volumes of carbon dioxide (CO2), the most common of GHG. Large CO2 emissions, together with fulfilling EU climate targets, are currently some of the main drivers for CCS technology adoption within the Baltics.
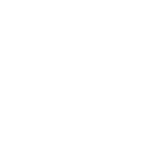
The CO2 will be captured at cement plants operated by Schwenk Latvija (LV) and Akmenės Cementas (LT).
Captured CO2 will be transported via CO2 newly designed pipeline to Klaipedos Sea Port. Amber grid (LT) and Conexus Baltic Grid (LV) will ensure smooth onshore transportation.
CO2 will be transported to and stored at the multimodal LCO2 import/export terminal operated by KN Energies located at Klaipėda port, Lithuania. Facility will accommodate acceptance of road transport by trucks or railway by wagons for small-medium volumes.
LCO2 will be transported by ships to the permanent offshore storage facility location. Mitsui O.S.K. Lines and Larvik Shipping will cover offshore transportation.
CCS Baltic Consortium project value chain
Covered by the Baltic CCS Consortium PCI